There is one topic that comes up time and time again. My internet speed is slow! But is it really? So let’s say you have Spectrum internet and your plan is 200/Mbps. That number represents the maximum download speed you will get for what you are paying for ‘IF’ certain criteria are met.
Notice the big IF in that statement? That is not your wifi speed, that is the speed for your computer if it is hardwired into your Spectrum Router. That is also assuming that your computer has a network interface that supports that speed as well. 10/100 which is an older technology will max out at 100/Mbps. Most network interfaces now are 10/100/1000 so if your computer has that, then you will definitely get to use all 200/Mbps of your download speed.
But most of us don’t have networking cabling running throughout our homes and we rely on Wifi. Now Wifi speeds are a lot slower than if you are using a cable. Believe it or not but some of the first wifi capable devices were anywhere between 2 and 11/Mbps. Technology got a little better and soon we had 54/Mbps. Now we are seeing Wifi devices using better protocols that are seeing speeds of 150 to 300/Mbps. Here is that IF again, but that is only IF you are standing right next to your Wifi router from Spectrum. You see, the further you are away from the device and the more things you put in between you and the Wifi router the slower and slower your Wifi speeds will be.
I often ask people, where is your wifi router in relation to where you were at the time of the slow download speeds? The answer is usually that the person is on one side of the house and the Wifi router is on the other. Or upstairs and they are downstairs. Or in the front of the house and they are out back by the pool. So visualize that in your head for a minute. Think about the distance, think about all the walls, think about everything that is in between you and the Wifi router.
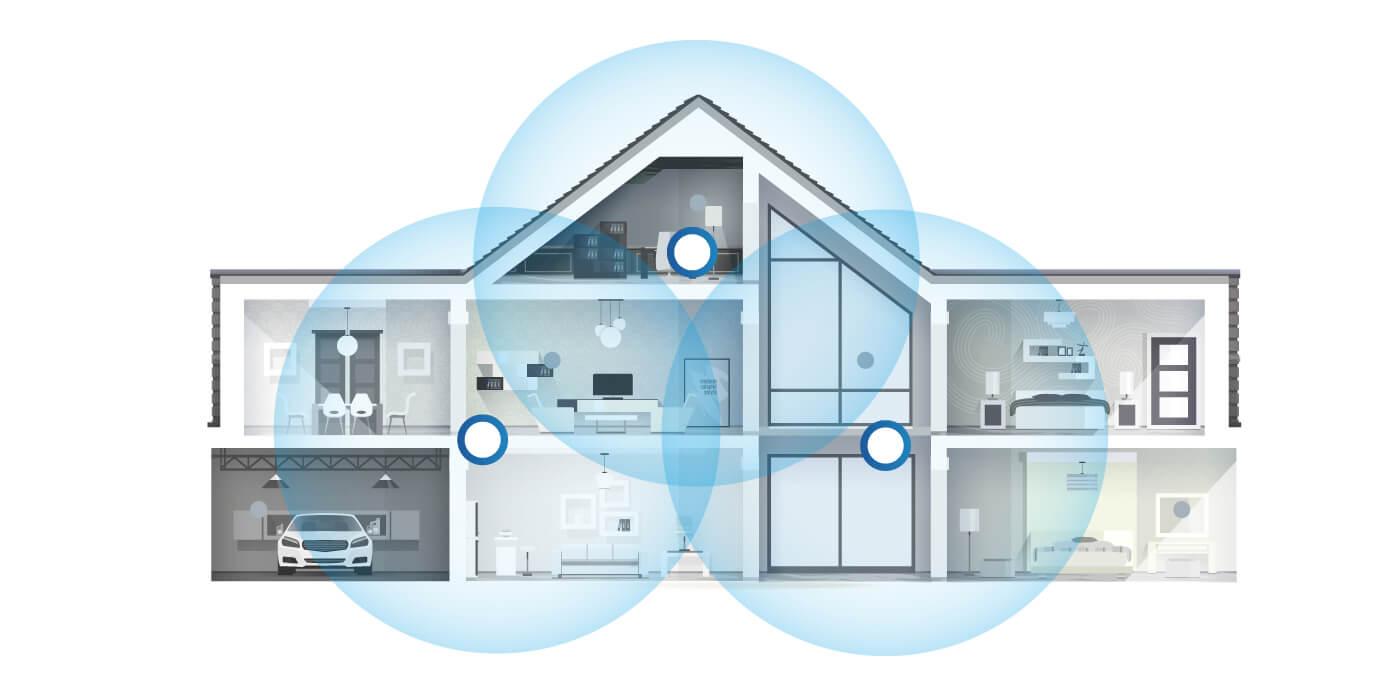
So how do we fix this problem? It’s called a Network Mesh.
A mesh network is a type of wireless network that is designed to provide reliable and seamless connectivity across a wide area. In a mesh network, multiple nodes or devices are used to transmit data wirelessly to each other, forming a web or mesh of connections.
Unlike traditional wireless networks, where each device is connected to a central router or access point, mesh networks allow devices to communicate directly with each other. This means that data can be transmitted across multiple paths, allowing for more efficient and reliable communication.
In a mesh network, each node is capable of relaying data to other nodes, ensuring that even if one node fails or goes offline, data can still be transmitted through other nodes in the network. This makes mesh networks highly resilient and reliable.
Mesh networks are often used in large, complex environments such as industrial sites, smart cities, or large buildings. They are also becoming increasingly popular in home networking, as they can provide better coverage and more reliable connectivity than traditional Wi-Fi networks.
Overall, the key benefits of mesh networks are their reliability, flexibility, and scalability, which make them an ideal solution for large, complex environments where traditional networking solutions may not be sufficient.